Git Commands
Git Install (Ubuntu)
1) Terminal (ctrl + Alt + T)
2) sudo apt install git
3) git --version
1.1 Git Commands
| Category | Command | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Create a new repo | $ git init | Create a .git subdirectory |
| Copy repo/Download(clone) | $ git clone <https://…URL> | Download/Copy existing source code |
| Add and Commit (add&commit) | $ git add | Add changes in a specific file (added to index) |
| $ git add -A | Add changes in all the files | |
| $ git commit -m “_message” | Create a commit (Finalize changes made) | |
| $ git status | Check file status | |
| Branch | $ git branch | List of branches |
| $ git branch | Create a new branch (set as local) | |
| $ git checkout -b | Create/Move to a branch | |
| $ git checkout master | Return to master branch | |
| $ git branch -d | Delete branch | |
| $ git push origin | Push the branch to remote repository | |
| $ git push -u | Push a new branch to the remote server’s repository | |
| $ git pull | Download the current status of the git project saved in the remote repository & merge to the current directory branch | |
| Publish/Push changes | $ git push origin master | Upload changes to remote repository |
| $ git push | Upload commit to remote repository | |
| $ git push -u | Upload commit to remote repository as a user | |
| $ git push -f | Force upload commit to remote repository | |
| $ git remote add origin | Add/Issue cloud address | |
| $ git remote remove | Delete cloud address | |
| <Update & Merge(merge)> | $ git pull | Fetch changes in remote repository and merge it to current directory |
| $ git merge | Merge changes in another branch to current branch | |
| $ git add | Merge a file | |
| $ git diff | Compare changes before merge | |
| Tag | $ git log | Check commit contents in current branch / Grant identifier |
| Roll back | $ git checkout – | Roll back to before change |
| $ git fetch origin | Download current status of a git project saved in remote repository |
1.2 Add vs.Commit vs. Push
Add:
- selects changes
- tells git to start tracking a file.
- If you modify a file after you run git add, you have to run git add again to stage the latest version of the file.
Commit:
- records changes LOCALLY
- saves the changes only to the local repository but not to the remote repository
- If you make any changes or even delete the files, you can still recover our committed files
Push:
- shares changes
- updates your committed changes and allows you to send them to the remote repository where all of the developers can access them
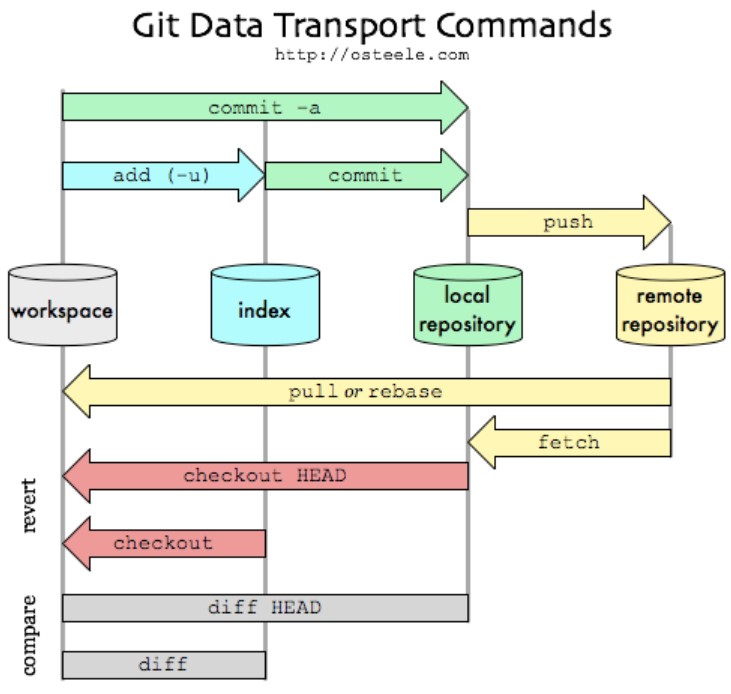
Image source: https://blog.osteele.com/2008/05/my-git-workflow/
